As we continue a closer look at the Strategic Network, the principle of Action and Expression or the How of Learning we are ready to move to guideline 5! We previously focused on guideline 4 associated with the principle of action and expression: options for physical action (see article) Universal Design for Learning: Deeper Dive 4. For more information on the other preceding guidelines associated with the recognition network see guideline 1: options for perception: Universal Design for Learning: Taking a Deeper Dive, guideline 2: options for language, mathematical expressions, and symbols: Universal Design for Learning: Taking a Deeper Dive 2 and guideline 3: options for comprehension: Universal Design for Learning: Deeper Dive 3.
Quick Recap about UDL: Starting with the base knowledge that Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework for designing and delivering instruction based on the three networks of the brain associated with learning:
1. The Recognition Network or the What of learning
2. The Strategic Network or the How of learning
3. The Affective Network or the Why of learning (CAST 20012)
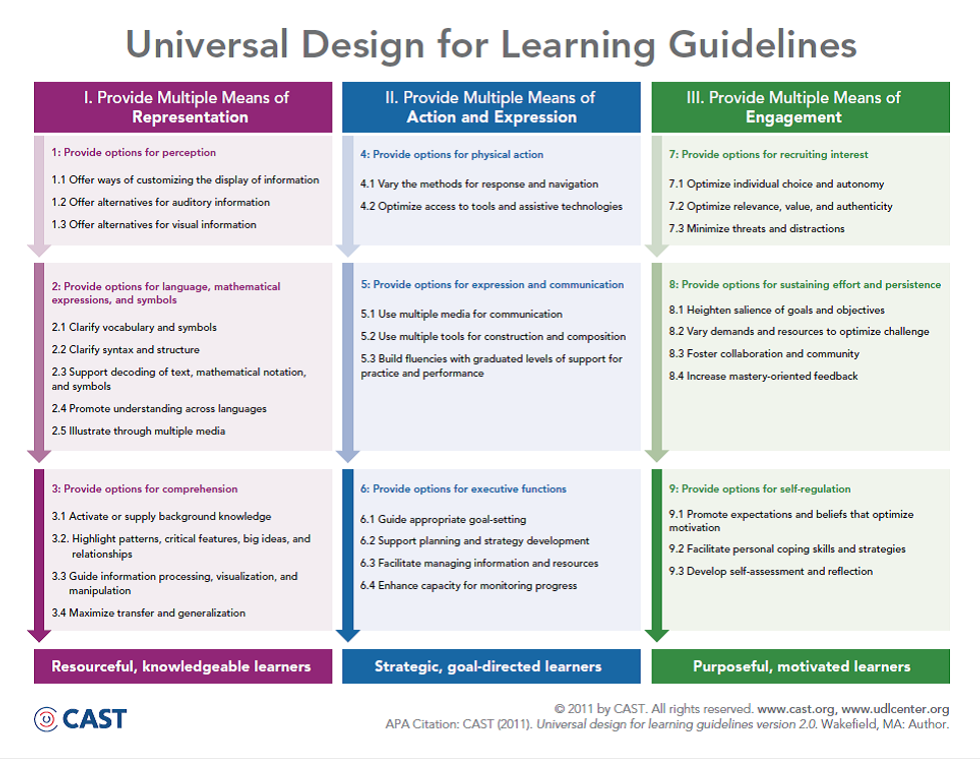
The three broad networks support the three principles of UDL (I) Provide multiple means of representation; (II) provide multiple means of action and expression; and (III) provide multiple means of engagement” (Rose & Meyer, 2002) and the subsequent nine guidelines (diagram below).
We now move to guideline 5: options for expression and communication associated with the strategic networks of the brain. The principle of Action and Expression, according to Lord Nelson, is about providing opportunities to students as they practice goal setting, planning, strategy building, organizing and using formation and resources, and monitoring their own progress in these areas (p. 79).
It is important to note here that the principle of action and expression is about much more than assessment. Therefore, the “strategic networks are what allow students to piece together and then demonstrate what they know” (Lord Nelson p. 84). To that end; students should be afforded many opportunities to practice with options and scaffolding available to support the process and interaction of the students with the skill and/or content.
Let’s zero in on our second of three guidelines under the principle of action and expression: guideline 5: options for expression and communication (below).
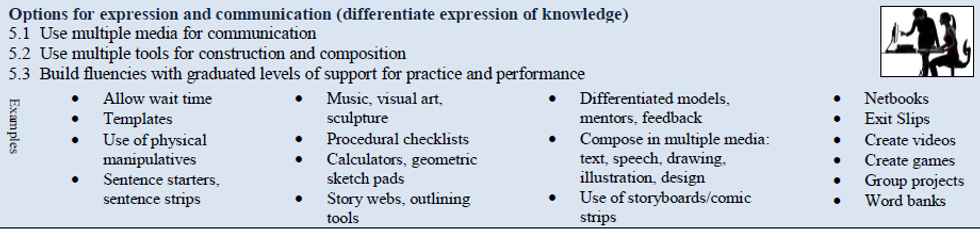
What: Options for expression and communication simply put are options to differentiate expression of knowledge. That knowledge can be based on content or skill. Designing for and providing students with options to express knowledge, ideas, skills, and concepts prevent the means from being embedded in the goal of demonstration or expression of understanding. This guideline is about providing multiple means to create and express knowledge for composition, problem solving, and fluency. Novak (p. 59) translates this guideline in elementary and secondary language respectively:
| “This will not be a class where we only take multiple-choice tests at the end of every unit. I want everyone to feel comfortable performing skits, making posters, and playing learning games. After we learn a new skill, you will have a number of choices about how you will express your knowledge to me.” |
|
How: By intentionally attending to barriers to expression of understanding educators can consider learner variability. Possible variabilities to consider are:
Beginning with a few simple questions can assist in the process of intentional design:
- Are there multiple ways for students to show what they know and can do?
- Have I provided access to tools to support creation of products?
- Have I provided scaffolding, examples and models to improve student performance?
Possible options to provide are:
Why: Providing options in action and expression benefits the learning process and subsequent outcomes on many levels. First and foremost it removes unsolicited demands on learning and the expression and demonstration of the learning outcome. Because the brain is goal directed, we must remember to not introduce and remove any unintended barriers from the learning goal. When we embed the means or the “way” in which students are to demonstrate and express their understanding, the goal quickly becomes an assessment of the means and not the actual content or skill we are attempting to assess. When content and skill acquisition are supported with scaffolding, resources, options, and support in a failure safe environment with many options and opportunities to practice, students are more effective and confident in their own knowledge and understanding regardless of the context in which they are placed to ultimately demonstrate their learning. You say “But what about standardized testing? There are no choices or options there!” The most poignant words about this argument come from the words of Jon Mundorf, “I'd rather teach effectively 180 days an ineffective test than teach ineffectively 180 days for an ineffective test!"
CAST, Inc. (2012) Retrieved from: http://www.udlcenter.org/aboutudl/whatisudl
Meyer, A., Rose, H. D., Gordon, D. (2014). Universal Design for Learning, theory and practice. Wakefield, MA: CAST Professional Publishing.
Lord Nelson, Loui. (2014) Design and Deliver: Planning and Teaching Using Universal Design for Learning. Baltimore, MD: Brookes Publishing.
Novak, Katie. (2014)) UDL Now. Wakefield, MA: CAST Publishing.